Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Benefit can enhance modern technology and advancement in a number of ways, and this includes Personalized learning environments, computerized grading schemes are a few examples of applications that offer assistance and direction. These technological advancements can improve the caliber and accessibility of education.
But have you ever wondered what Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are actually used for, what their functionalities are and how to use them. This content is really going to explain everything you need to know and also explain the life phases of ML projects, so the next time you’re building an app that uses some amazing, new AI/ML-based service, you understand what’s behind it and what makes it so amazing.
INTRODUCTION TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND MACHINE LEARNING

WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Artificial Intelligence refers to the imitation of human intelligence in devices that have been designed to have human-like thought and learning processes. It entails building computer systems that are capable of carrying out operations like speech recognition, visual perception, problem solving, and decision-making that ordinarily call for human intellect. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a vast field with many subfields, such as computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning. This is an intriguing field of technology that is still developing and has the power to completely transform a wide range of sectors.
KEY COMPONENTS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Key components refers to or describes a basic component or piece that is necessary for AI systems to function, and they play significant roles. These elements work together like building blocks to increase AI’s overall capabilities. They Include :
- Machine Learning:
This is a branch of artificial intelligence used to create models and algorithms that let computers learn from data and make judgments or predictions without needing to be explicitly programmed. In order to produce precise predictions or take action, it entails training a machine learning model with a lot of data. The model discovers patterns and relationships in the data. It’s analogous to educating a computer to identify patterns and draw conclusions from them. Applications for machine learning include speech and picture recognition, recommendation engines, and even self-driving automobiles. The ability of machines to learn and become more proficient over time is quite remarkable.
2. computer vision:
The goal of the artificial intelligence field of computer vision is to empower computers to recognize and analyze visual data from pictures or movies. It entails creating methods and algorithms that let computers derive useful information from visual data, including item identification, face recognition, motion detection, and even scene context. Applications for computer vision are numerous and include augmented reality, medical imaging, surveillance systems, and driverless cars. It’s similar to giving computers eyes and minds to perceive and comprehend their surroundings.
3. natural language processing:
natural language processing (NLP) is to enable computers to comprehend, interpret, and communicate with human language in a meaningful and natural way. It entails creating models and algorithms that let computers process and examine speech or text, extract pertinent data, and produce relevant responses. . It’s similar to educating computers to comprehend human language and interact with us in that way. The way that NLP is influencing our interactions with technology is really fascinating.
4. knowledge representation:
knowledge representation studies ways to organize and represent knowledge so that machines may comprehend it and utilize it as a tool for reasoning. It entails building models or frameworks that record data and the connections between various concepts or entities. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems may store and retrieve knowledge, draw conclusions, and solve issues using these representations. It’s similar to creating an organized framework for knowledge processing and storing in computers. The application of these representations by AI systems to improve comprehension and decision-making skills is really massive.
5. Reasoning:
The process of applying logical analysis and reasoning to solve issues is known as reasoning. It entails applying the facts, evidence, and knowledge currently available to reach a reasonable and logical conclusion. Reasoning is a key component of artificial intelligence, which enables machines to carry out tasks and make judgments based on the information at hand.
TYPES OF AI
- 1. Narrow AI: Also referred to as weak AI, narrow AI is intended to carry out particular duties or operations. Voice assistants such as Alexa or Siri, recommendation engines, and image recognition algorithms are a few examples.
- General AI: Also called powerful AI, general AI strives to be intelligent enough to understand, study, and carry out any intellectual work that a human is capable of.
- Machine Learning: This branch of artificial intelligence focuses on creating models and algorithms that let computers utilize data to learn and make predictions or judgment calls. It makes it possible for systems to advance and change without explicit programming.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that makes use of artificial neural networks for prediction and learning. Particularly successful applications of it include speech and picture recognition.
APPLICATION OF AI
Application of AI torches many sectors and domains. It all comes down to how AI is used to solve issues, automate chores, and improve the effectiveness of operations. AI may be used to improve decision-making, increase accuracy, and offer tailored experiences in a variety of industries, including healthcare, banking, transportation, and e-commerce. The following are some application areas where AI is having a big influence:
- Healthcare: This helps in analysis, assisting in the early detection of diseases and viruses such as Cancer and other deadly infections.
- Finance: AI assists in risk assessment and fraud detection. It also supports models that evaluate creditworthiness by examining a range of financial and non-financial variables.
- Education: Artificial Intelligence (AI) not only helps grade assignments and tests automatically, but also customizes educational materials to each student’s unique learning style and speed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Conversational agents driven by AI offer assistance and support to customers as well as multilingual text and voice translation.
- Driverless Automobiles: AI systems use sensor data to guide and facilitate control over driving decisions. In large, smart cities, it also aids in reducing traffic jams and optimizing traffic flow.
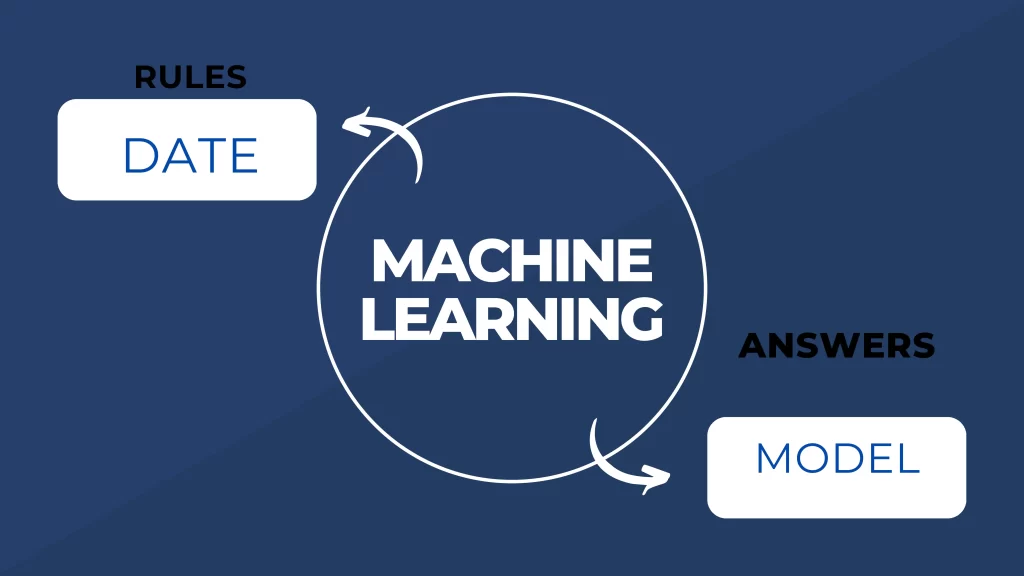
WHAT IS MACHINE LEARNING
The process of applying logical analysis and reasoning to solve issues, reach conclusions, or draw inferences is known as reasoning. It entails applying the facts, evidence, and knowledge currently available to reach a reasonable and logical conclusion. Reasoning is a key component of artificial intelligence, which enables machines to carry out tasks and make judgments based on the information at hand. It’s similar to making connections between ideas and following reasoning to arrive at a conclusion. An essential component of human intelligence is reasoning, which artificial intelligence (AI) aims to duplicate and improve in robots.
KEY COMPONENTS OF MACHINE LEARNING
- Algorithms: The data is processed, patterns are found, and predictions or choices are made using machine learning algorithms. Various kinds of issues lend themselves to different kinds of algorithms.
- Model: The machine learning algorithm generates a model that illustrates the correlations and patterns that are discovered through data analysis. It can be applied to categorize fresh data or generate predictions.
- Training: Labeled data is fed into the model to help it learn from the patterns and produce precise predictions.
- Data: To train machine learning models, relevant and high-quality data is required. The model learns patterns and relationships from the data.
- Evaluation: To determine the model’s performance after training, evaluation is required. This is accomplished by evaluating the model’s efficacy and accuracy using a different dataset.
TYPES OF MACHINE LEARNING
- Supervised Learning: This kind of learning uses labeled data to train a model in which the input data is matched with the appropriate output, after studying these instances, the model has the ability to forecast or categorize previously unobserved data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Utilizing unlabeled data, unsupervised learning differs from supervised learning. Without any predetermined labels, the model discovers structures, relationships, and patterns in the data. It can be applied to dimensionality reduction and clustering tasks.
- Reinforcement learning: Using trial and error, an agent is trained to interact with its surroundings and learn new skills. Based on its behaviors, the agent receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties, which enables it to learn the best practices or policies.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: In this method, aspects of unsupervised and supervised learning are combined. To train the model, a smaller amount of labeled data and a greater number of unlabeled data are used. When classifying data is costly or time-consuming, this can be helpful.
- Transfer Learning: Transfer learning involves leveraging knowledge or models learned from one task to improve performance on a different but related task. It can save time and resources by reusing pre-trained models.
APPLICATION OF MACHINE LEARNING

Machine Learning possesses an extensive range of usage and this includes :,Recommendation systems, fraud detection, natural language processing, image and audio recognition, and even driverless cars employ it. Large-scale data analysis is a capability of machine learning algorithms, which they use to learn and forecast, categorize, or produce insights. The use of machine learning to address challenging issues and improve our quality of life is really fascinating. Here are a few noteworthy uses of machine learning:
- Medical: Illness Diagnosis: To aid in the diagnosis of diseases, machine learning algorithms examine medical data, including genetic and imaging data.
- Personalized Care: ML facilitates the customization of treatment regimens according to the unique traits and reactions of each patient.
- Finance: Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms detect trends that point to potential fraud in financial transactions.
- Credit Scoring: ML algorithms examine a range of financial and non-financial variables to determine a borrower’s creditworthiness.
- Retail: Suggestion Systems: ML drives customer-specific product suggestions based on their behavior and interests.
- Demand Forecasting: By projecting future product demand, machine learning models maximize inventory control.
- Marketing: consumer Segmentation: ML facilitates the creation of consumer segments for focused marketing campaigns based on behavior and preferences.
- Predictive analytics: ML models forecast consumer patterns and behavior to guide advertising campaigns.
- Production and Predictive Maintenance: To save downtime, machine learning (ML) examines equipment data to forecast when maintenance is necessary.
ALGORITHMS AND MODELS
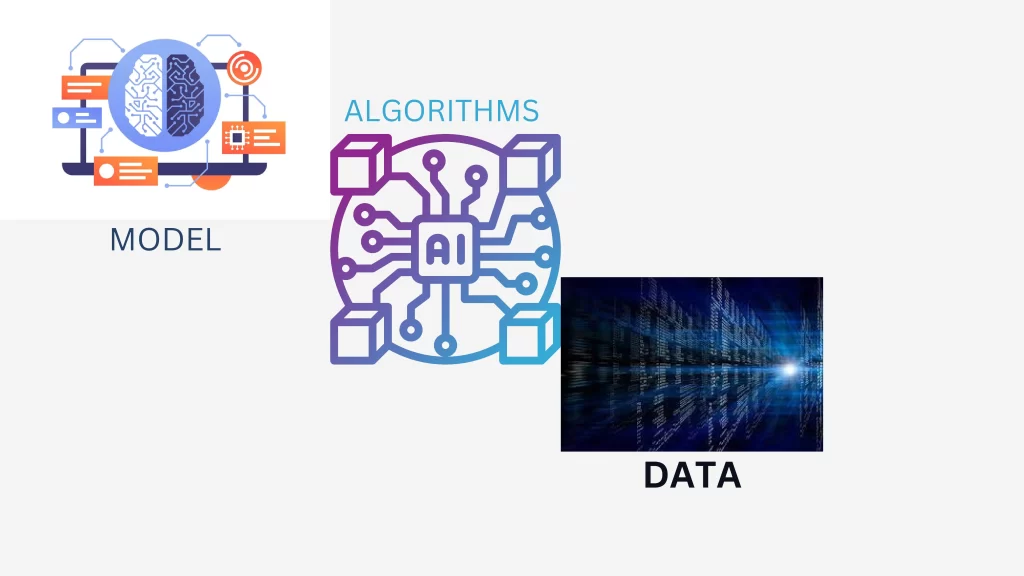
Algorithms are a set of guidelines or directives that a computer program adheres to in order to carry out a task or address a particular issue in the context of artificial intelligence and machine learning. They function as the fundamental components of models for machine learning. Machine learning models, on the other hand, are mathematical depictions of the relationships and patterns found in data.
In other words, models are the learnt representations of data that allow for prediction and decision making, whereas algorithms offer the framework for problem solving. Together, they enable machine learning systems to be strong and efficient.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
In fact, ethical issues are very important when it comes to AI and ML. As these technologies grow more sophisticated and widespread, it’s critical to address concerns about accountability, transparency, privacy, and prejudice. AI and ML systems must be impartial, fair, and considerate of people’s rights. The development of ethical frameworks and rules to direct the appropriate use of AI and ML is a topic of continuing discussion in the area. When developing and implementing new technologies, it’s critical to keep society in mind and pursue moral standards.
BENEFITS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND MACHINE LEARNIG
There are several advantages to AI and ML, including the ability to automate monotonous jobs, increase productivity, and improve decision-making. Large volumes of data may be properly and swiftly analyzed by AI, producing insightful predictions. ML algorithms provide ongoing optimization and improvement by learning from data and adapting. Additionally, these technologies can improve personalization through customized learning experiences or recommendations. AI and ML also have the power to completely transform sectors of the economy like banking, healthcare, and transportation. The opportunities are fascinating and in the nearest future the transformation of AI and ML will have a significant impact on students in west African Countries.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTION

- what is Intelligence and Machine learning:
. It involves the ability to comprehend, reason, acquire knowledge, and work through issues. Contrarily, machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on giving computers the ability to learn and make judgments without explicit programming. It uses algorithms to examine data, spot trends, and come at well-informed conclusions or forecasts. Through data-driven learning, computers can gradually increase their performance thanks to machine learning.
2.what can Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning be used for :
Numerous applications exist for AI and ML, such as intelligent tutoring systems that offer support and advice, automated grading systems, and personalized learning platforms.
3.what is the difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning:
Although they are both subfields of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) differs in a few ways. It entails drawing conclusions from fresh, untainted data and training models on labeled data. However, deep learning (DL) is a subset of machine learning (ML) that uses multiple-layered artificial neural networks—thus the word “deep”—to identify and extract intricate patterns from data. Particularly successful applications of DL are image and speech recognition.







